Which of the following is an example of a census? This intriguing question opens the door to a comprehensive exploration of the concept and significance of censuses. A census is a large-scale, systematic enumeration of a population, providing valuable data that shapes decision-making and resource allocation.
Throughout history, censuses have played a crucial role in understanding population dynamics, informing policies, and ensuring equitable distribution of resources. From ancient civilizations to modern nation-states, censuses have evolved in their methods and scope, but their fundamental purpose remains the same: to provide a comprehensive snapshot of a population at a specific point in time.
Definition of Census: Which Of The Following Is An Example Of A Census

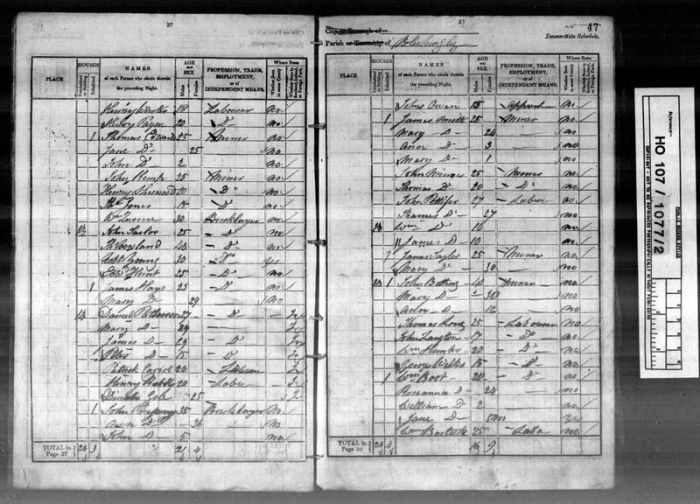
A census is a comprehensive enumeration of a population, typically conducted by a government agency. It involves collecting detailed information about each individual, household, or establishment within a defined geographic area. Censuses provide a snapshot of a population’s characteristics, such as age, gender, education level, employment status, and housing conditions.
Types of censuses include population censuses, economic censuses, agricultural censuses, and housing censuses. Each type of census focuses on specific aspects of the population or economy.
Purpose of Census
The primary objective of a census is to provide comprehensive and accurate data about a population. This data is essential for:
- Planning and allocating resources for public services, such as education, healthcare, and infrastructure.
- Understanding population trends and changes, such as growth rates, migration patterns, and aging.
- Formulating policies and programs that address the needs of different population groups.
- Monitoring the effectiveness of government programs and interventions.
Methods of Census

There are several methods used for collecting census data:
Traditional Census
Involves enumerators visiting households or establishments in person to collect information.
Mail-In Census
Involves sending questionnaires to households or establishments by mail, which are then returned to the census agency.
Online Census, Which of the following is an example of a census
Involves completing the census questionnaire online through a secure website.
Combined Methods
Involves using a combination of methods, such as mail-in and online census, to reach different population groups.
Examples of Census
| Country | Purpose | Scope | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Population count and characteristics | All residents | Every 10 years |
| India | Population count and socio-economic data | All residents | Every 10 years |
| United Kingdom | Population count and demographics | All residents | Every 10 years |
| China | Population count and economic data | All residents | Every 10 years |
Importance of Census Data
Census data is valuable for various stakeholders, including:
- Government agencies: For planning and implementing public policies and programs.
- Businesses: For market research, site selection, and workforce planning.
- Researchers: For studying population trends, social issues, and economic development.
- Non-profit organizations: For identifying needs and targeting services to vulnerable populations.
- Individuals: For understanding their community and accessing government benefits and services.
FAQs
What is the primary purpose of a census?
The primary purpose of a census is to provide a comprehensive and accurate count of a population, including its size, composition, and distribution.
How often are censuses conducted?
The frequency of censuses varies from country to country, but they are typically conducted every 5 or 10 years.
What are some examples of how census data is used?
Census data is used for a wide range of purposes, including planning for healthcare, education, transportation, and housing; redistricting electoral boundaries; and allocating government funding.