Which statements describe geologic gaps check all that apply – Which statements describe geologic gaps? Check all that apply embarks on an intellectual odyssey, inviting readers to delve into the enigmatic realm of Earth’s geologic tapestry. This discourse unravels the mysteries of geologic gaps, illuminating their profound significance in deciphering our planet’s captivating history.
Geologic gaps, like elusive whispers from the depths of time, hold tantalizing clues to past environmental conditions and tectonic upheavals. They challenge us to piece together the fragmented narrative of Earth’s evolution, offering glimpses into epochs long vanished.
Definition of Geologic Gaps
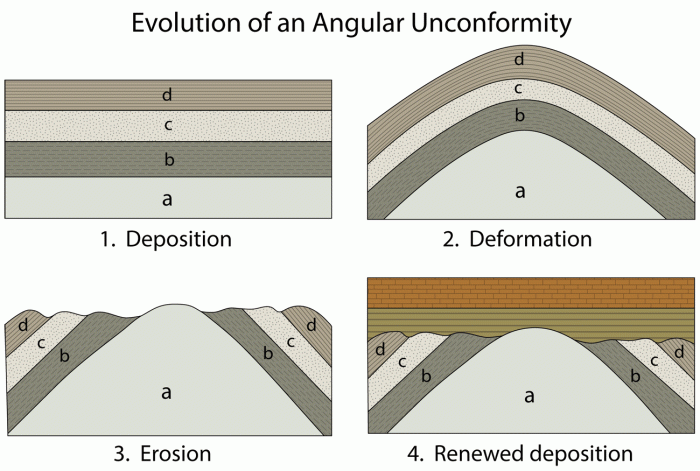
Geologic gaps refer to intervals of time that are not represented in the geologic record due to the absence of sedimentary or igneous rocks. These gaps can range in duration from a few years to millions of years and can provide valuable insights into Earth’s history.
Geologic gaps are identified by comparing the geologic record of different areas or by examining the sequence of rock layers in a single location. When a significant time interval is missing from the record, it is inferred that a gap exists.
Types of Geologic Gaps
- Unconformities: These are gaps that represent a break in the deposition of sedimentary rocks. They can be caused by erosion, tectonic activity, or changes in sea level.
- Hiatuses: These are gaps that represent a period of non-deposition. They can be caused by a variety of factors, including changes in climate, sea level, or the availability of sediment.
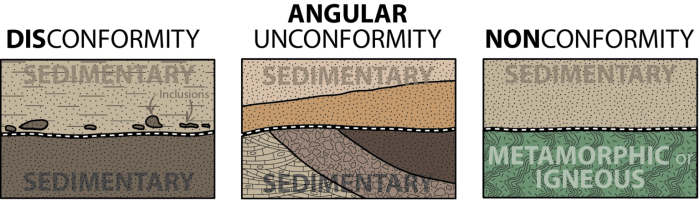
- Disconformities: These are gaps that represent a period of erosion. They are typically found at the contact between two different types of rock, such as sedimentary and igneous rocks.
Causes of Geologic Gaps
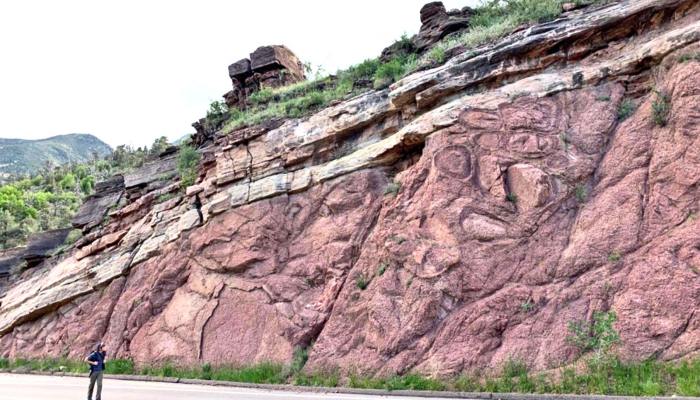

Geologic gaps can be caused by a variety of processes, including:
Erosion
Erosion is the process of wearing away the surface of the Earth by wind, water, or ice. Erosion can remove entire layers of rock, creating gaps in the geologic record.
Deposition
Deposition is the process of laying down new sediment. Deposition can fill in gaps in the geologic record, but it can also create new gaps by burying older rocks.
Tectonic Activity, Which statements describe geologic gaps check all that apply
Tectonic activity can create gaps in the geologic record by uplifting or folding rocks. This can expose older rocks to erosion or make them inaccessible for study.
Climate Change
Climate change can also contribute to the formation of geologic gaps. For example, changes in sea level can cause erosion or non-deposition, creating gaps in the sedimentary record.
Significance of Geologic Gaps
Geologic gaps are important for understanding Earth’s history because they can provide insights into past environmental conditions.
For example, gaps in the sedimentary record can indicate periods of time when the climate was too hot or too cold for life to thrive. Gaps can also provide information about the movement of continents and the formation of mountain ranges.
In addition, geologic gaps can be used to identify and assess geological resources. For example, gaps in the coal record can indicate areas where coal is likely to be found.
Methods for Analyzing Geologic Gaps: Which Statements Describe Geologic Gaps Check All That Apply
| Method | Principle | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Field Observations | Direct examination of rock outcrops and drill cores | Provides detailed information about the nature and extent of gaps | Can be limited by accessibility and exposure |
| Geophysical Surveys | Use of seismic waves, gravity, or magnetic fields to map subsurface structures | Can provide information about gaps that are not exposed at the surface | Can be expensive and difficult to interpret |
| Stratigraphic Analysis | Comparison of rock layers from different locations | Can help to identify and correlate gaps | Can be difficult to apply in areas with complex geology |
| Paleontological Analysis | Study of fossils to determine the age and environment of rock layers | Can provide information about the timing and duration of gaps | Can be limited by the availability of fossils |
Applications of Geologic Gap Analysis
Geologic gap analysis has a variety of practical applications, including:
Mineral Exploration
Gaps in the geologic record can indicate areas where mineral deposits are likely to be found. For example, gaps in the coal record can indicate areas where coal is likely to be found.
Environmental Assessment
Gaps in the geologic record can provide information about past environmental conditions. This information can be used to assess the potential impacts of future environmental changes.
Geotechnical Engineering
Gaps in the geologic record can indicate areas where there is a risk of landslides or other geotechnical hazards. This information can be used to design and construct safe buildings and infrastructure.
FAQs
What are geologic gaps?
Geologic gaps are intervals in the geologic record where there is no preserved sedimentary or rock record.
How are geologic gaps identified?
Geologic gaps are identified by comparing the ages of rocks on either side of the gap.
What are the different types of geologic gaps?
There are two main types of geologic gaps: disconformities and nonconformities.
What causes geologic gaps?
Geologic gaps can be caused by erosion, deposition, or tectonic activity.
What is the significance of geologic gaps?
Geologic gaps provide important information about Earth’s history, including past environmental conditions and tectonic activity.