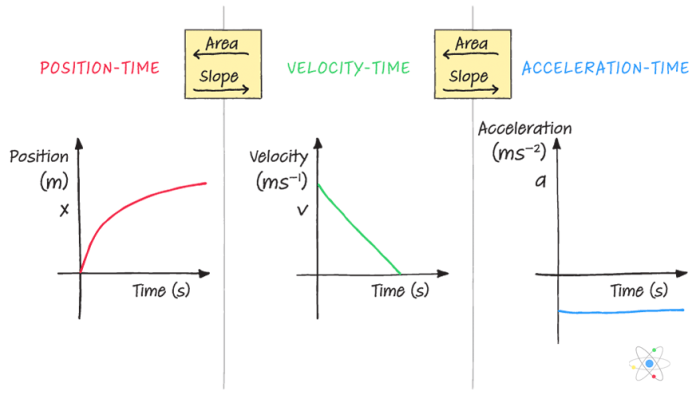
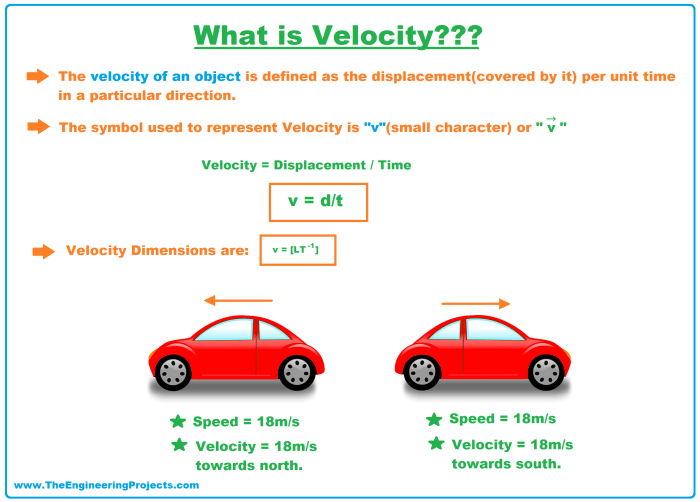
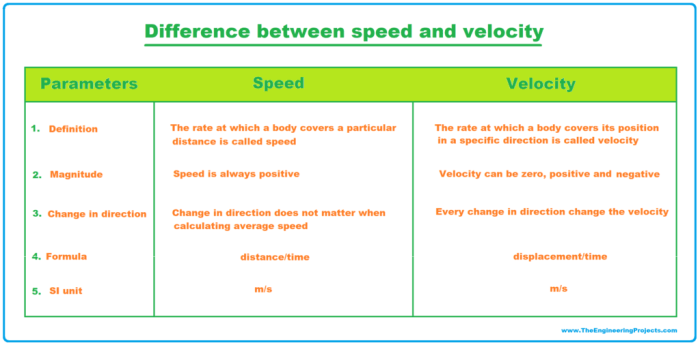
Which statements describe velocity and acceleration check all that apply – Velocity and acceleration are two fundamental concepts in physics that describe the motion of objects. Velocity is a measure of how fast an object is moving, while acceleration is a measure of how quickly an object’s velocity is changing. Both velocity and acceleration are vector quantities, meaning they have both magnitude and direction.
In this article, we will discuss the definitions of velocity and acceleration, provide examples of each, and explain the relationship between the two concepts.
Velocity is defined as the rate of change of displacement. Displacement is a vector quantity that describes the change in position of an object. Velocity is a vector quantity that describes the rate at which an object’s position is changing.
The SI unit of velocity is meters per second (m/s). Velocity can be positive or negative. A positive velocity indicates that the object is moving in the positive direction, while a negative velocity indicates that the object is moving in the negative direction.
Velocity and Acceleration: Which Statements Describe Velocity And Acceleration Check All That Apply
Velocity and acceleration are two fundamental concepts in physics that describe the motion of objects. Velocity measures the rate of change of an object’s position, while acceleration measures the rate of change of an object’s velocity.
Velocity
- Velocity is a vector quantity that has both magnitude and direction.
- The magnitude of velocity is the speed of the object.
- The direction of velocity is the direction in which the object is moving.
- The SI unit of velocity is meters per second (m/s).
- Velocity is related to displacement and time by the following equation: velocity = displacement / time
Acceleration
- Acceleration is a vector quantity that has both magnitude and direction.
- The magnitude of acceleration is the rate at which the object’s speed is changing.
- The direction of acceleration is the direction in which the object’s speed is increasing.
- The SI unit of acceleration is meters per second squared (m/s^2).
- Acceleration is related to velocity and time by the following equation: acceleration = (final velocity – initial velocity) / time
Velocity and Acceleration Equations, Which statements describe velocity and acceleration check all that apply
The following equations can be used to solve problems involving velocity and acceleration:
velocity = displacement / time
acceleration = (final velocity- initial velocity) / time
Applications of Velocity and Acceleration
Velocity and acceleration are used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Science: Velocity and acceleration are used to describe the motion of objects in the universe, from the movement of planets to the flow of fluids.
- Engineering: Velocity and acceleration are used to design and control machines, from cars to airplanes.
- Everyday life: Velocity and acceleration are used to describe the motion of objects in our everyday lives, from the speed of a car to the acceleration of a roller coaster.
Questions Often Asked
What is the difference between velocity and acceleration?
Velocity is a measure of how fast an object is moving, while acceleration is a measure of how quickly an object’s velocity is changing.
What are the units of velocity and acceleration?
The SI unit of velocity is meters per second (m/s), while the SI unit of acceleration is meters per second squared (m/s^2).
What is the relationship between velocity and acceleration?
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity.